Since the introduction of Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) I've started to rely on it more and more, but there are still a few quirks when dealing with multiple environments that access the same repo on disk.
Some of the issues I've encountered are:
- Ensuring line-endings are properly handled on the mounted windows volumes
- Centralizing credential management
Let's tackle them one-by-one.
Ensuring line-endings are properly handled on the mounted windows volumes
After installing git in both WSL and Windows you'll notice that the default settings are different. Windows uses Carriage-Return - Line-Feed (CRLF) where Linux and thus WSL rely on Line-Feed only.
This won't cause any issues until you use git in WSL on a repo that's cloned by windows. Suddenly all your files are modified, since git sees that all the files in the working area have windows line endings, where it expects line feeds.
I used the conditional configuration includes to automatically load my windows .gitconfig for repositories that are stored on the windows drive that's mounted inside WSL:
# Settings that are true for all repos on the WSL volume go here:
[core]
autocrlf = false
# Then include the Windtows git config
[includeIf "gitdir:/mnt/c/"]
path = /mnt/c/Users/jesse/.gitconfig
# Then reset the ssl backend and editor which aren't available on Linux
[http]
sslbackend = gnutls
[core]
editor = nanoThis ensures that I'm always using the setting that matches the OS that owns these repos and keeps my sanity.
There are a few settings we must reset on the WSL side, because on Windows I use the Windows Secure Channel SSL backend, and I haven't figured out how to use that on the WSL side (yet).
Centralizing credential management
The other problem has to do with the fact that Git on Windows stores its passwords in the windows credential store (if you've enabled the Git Credential Manager).
Git on WSL however remains blissfully unaware of any such magic and will happily prompt for its own passwords. Until I stumbled upon this little gem in the WSL docs. With a few lines of configuration Git on WSL can call the credential manager on the Windows side to configure and fetch credentials.
When installing Git on windows, be sure to select you want to use the Credential Manager:
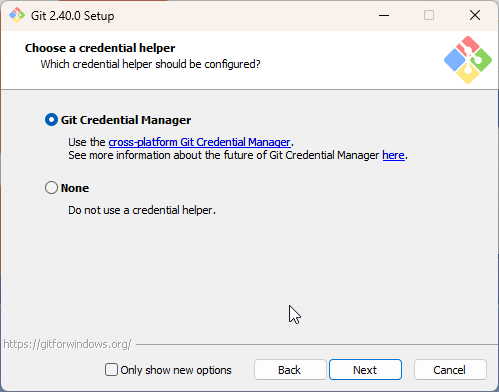
Select the installation of the Git Credential Manager (you may have to uncheck Only show new options). Then add the path to the credential-manager.exe to your WSL's .gitconfig:
[credential]
helper = /mnt/c/Program\ Files/Git/mingw64/bin/git-credential-manager.exeThis is where it resides on my machine, the path might be slightly different on yours.
Next time Git on WSL needs any credentials it will be able to grab them from the Windows Credential Manager instead, or pop-up a UI prompt to fill in the details.
Written by
Jesse Houwing
Jesse is a passionate trainer and coach, helping teams improve their productivity and quality all while trying to keep work fun. He is a Professional Scrum Trainer (PST) through Scrum.org, Microsoft Certified Trainer and GitHub Accredited Trainer. Jesse regularly blogs and you'll find him on StackOverflow, he has received the Microsoft Community Contributor Award three years in a row and has been awarded the Microsoft Most Valuable Professional award since 2015. He loves espresso and dark chocolate, travels a lot and takes photos everywhere he goes.
Contact
