Load testing is a technique that focuses on evaluating the performance of an application under normal or expected load conditions. The goal is to determine how the application behaves when it is subjected to the expected levels of usage and traffic. Load testing is often used to verify that a system can handle the expected number of users and transactions, and to identify any performance bottlenecks or issues that may impact the user experience.
Microsoft Azure offers a service called Azure Load Testing. One of the key benefits of using this service is that it allows you to test your application’s performance at a scale without having to invest in expensive hardware and infrastructure. Additionally, it is highly configurable and can be used to test applications hosted on a variety of platforms, including Azure, on-premises servers, and third-party cloud providers.
What do we need?
In addition to an Azure Subscription, and a GitHub account, we will need an Apache JMeter script, which typically consists of a series of test elements, including thread groups, samplers, listeners, and assertions. The thread groups define the number and type of virtual users that will be simulated, while the samplers define the specific actions or requests that will be performed by the virtual users. The listeners capture the performance data generated by the test, and the assertions define the expected results of the test and verify that the actual results match the expectations.
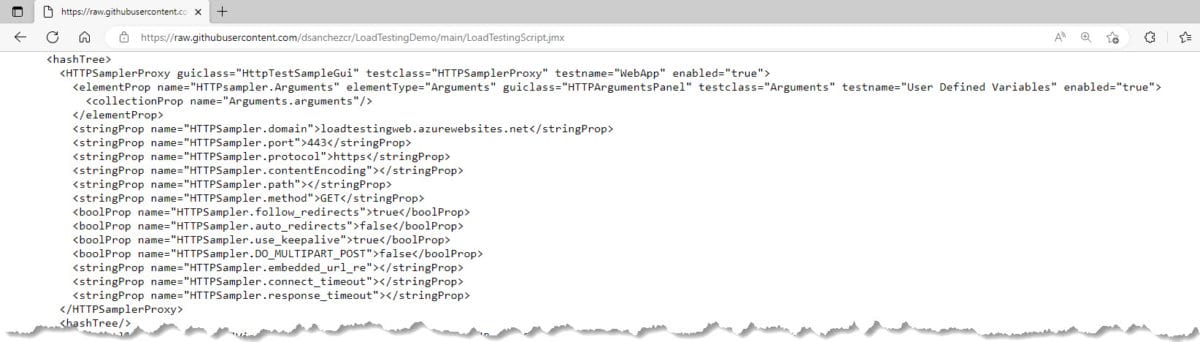
Here is an example of what the JMeter script looks like. You can find this script in the sample code that I created as part of this article (you can find the link below).
Getting Started
In the following example, we are going to use Azure Load Testing in our GitHub Actions workflow to detect when our web app has reached a performance issue. We are going to define a Load Test scenario with a specific number and type of virtual users that will be simulated, as well as the test duration and the type of workload to be simulated, which in this case is just an HTTP Request. In addition, you can also use either Visual Studio or the Azure Portal to create and configure your load test scenario.
Once the load test scenario is defined, we can review the results and the monitoring data, which includes metrics such as response time, CPU usage, and network traffic, as well as custom performance counters that we can define. With this data we identify bottlenecks and optimize the application’s performance.
The scenario
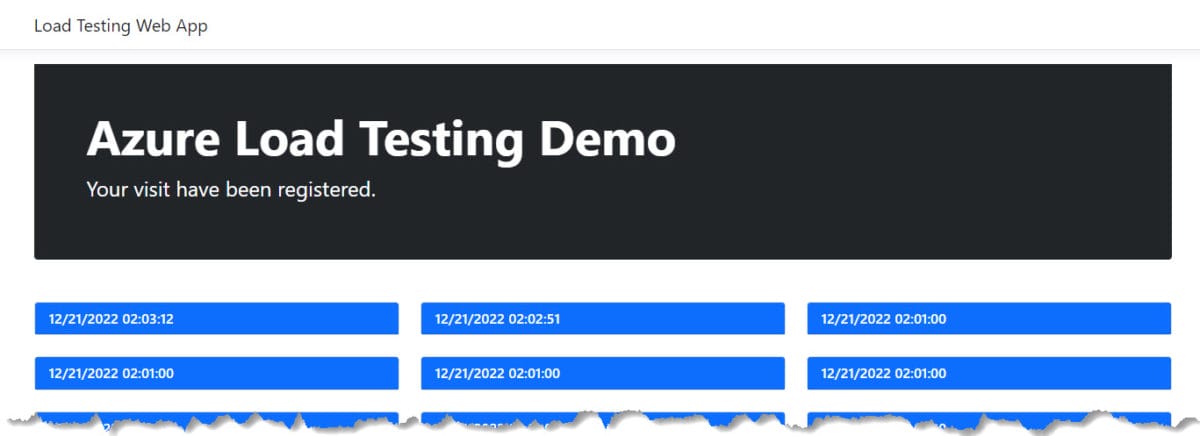
I developed a simple Web App built with ASP.NET Core using .NET 7 that connects to an Azure Cosmos DB and adds a record of each visit to the page and retrieves the data from all the visits.
Here is a screenshot of how the application looks like:

The environment
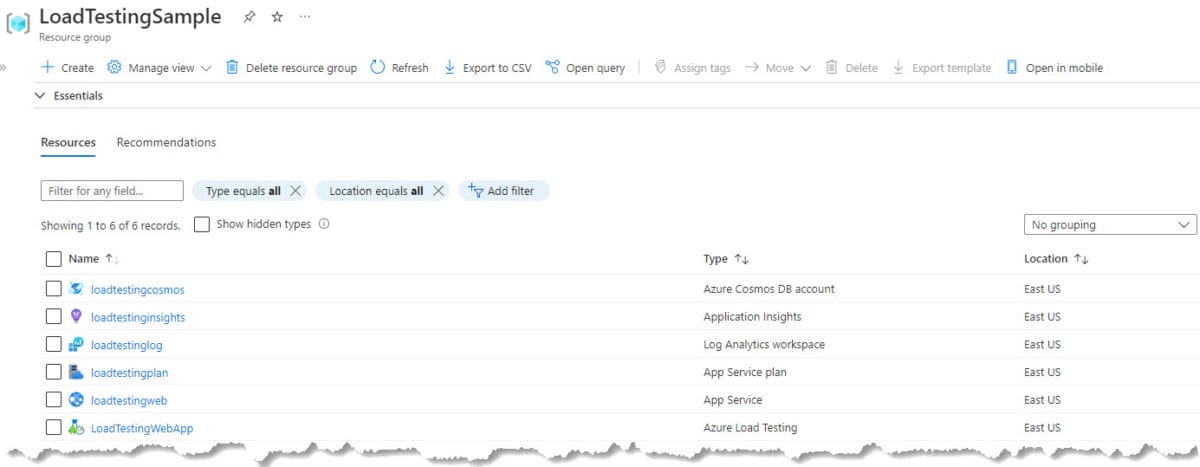
This web app is running on an App Service Basic plan, and it has Applications Insights to monitor the performance of the application. The Cosmos DB is set with the free tier (1000 RU/s and 25 GB). I want to find out if the application running in this environment can support up to 100 concurrent users.
Here is a screenshot of the Resource Group created with the Azure resources for this application.

The repository
You can check out the GitHub repository in this link (LoadTestingDemo). There you can fork the repository, use the ARM template to deploy the Azure services needed and run the Load Testing in your environment.
Note: Microsoft Azure only allows you to create one Cosmos DB Free Tier resource per subscription, you might get an error if you already have one Cosmos DB Free Tier in your subscription.
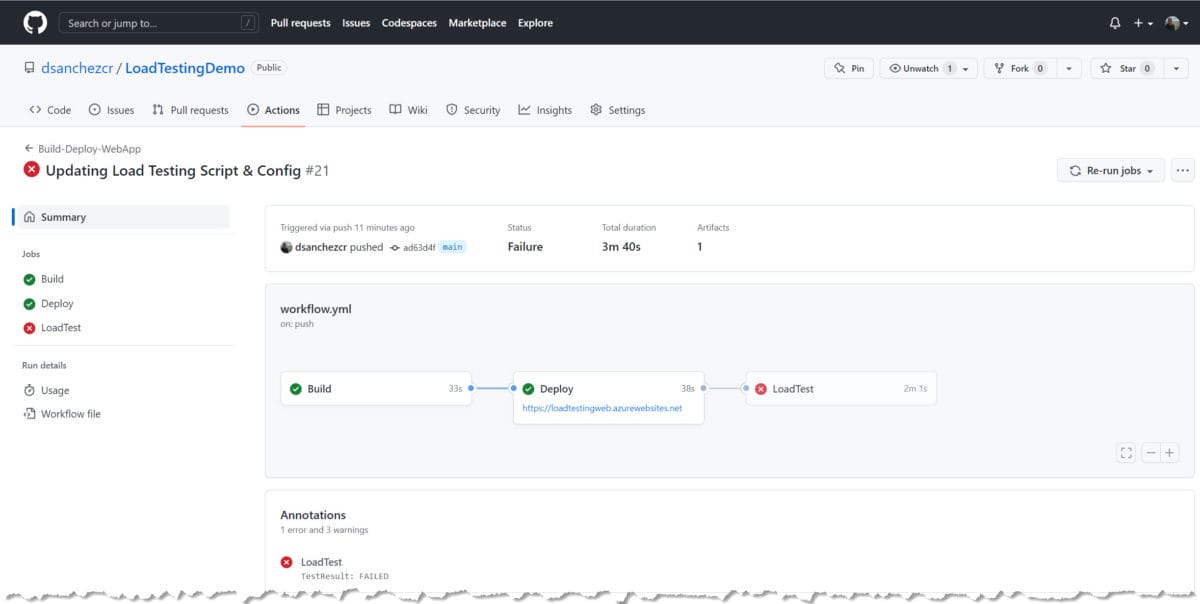
This repository has a GitHub Action that Builds & Deploys the application and runs the Load Test in Azure Load Testing. You can find the workflow in the Action tab of the repository.
Here is a screenshot of what the Action looks like. You can see it is failing in the LoadTest job.

The GitHub Action
The workflow consists of three steps and runs on every push. This first step builds the .NET application, the second step deploys the application to the Azure App Service and the third step runs the Load Test job using the following files that are in the root folder. The first file is the JMeter script used to specify the steps of the Load Testing, the second file is the configuration of the Load Testing.
- LoadTestingScript.jmx
- LoadTestingConfig.yaml
The Azure login is required to communicate with the Azure Load Testing service to send the JMeter script and the configuration for the test. In this configuration, we can define the number of engines we want to run the test and the failure criteria, in this case, the threshold we have is an average response time lower than 5 seconds and error percentage lower than 20%.
The Results
As you can see from the previous image, the Load Test failed because the average response time was higher than we expected (5 seconds). We can get more details about the test run in the Azure Portal.
Here is a screenshot of the result of the test run in the Azure Portal.
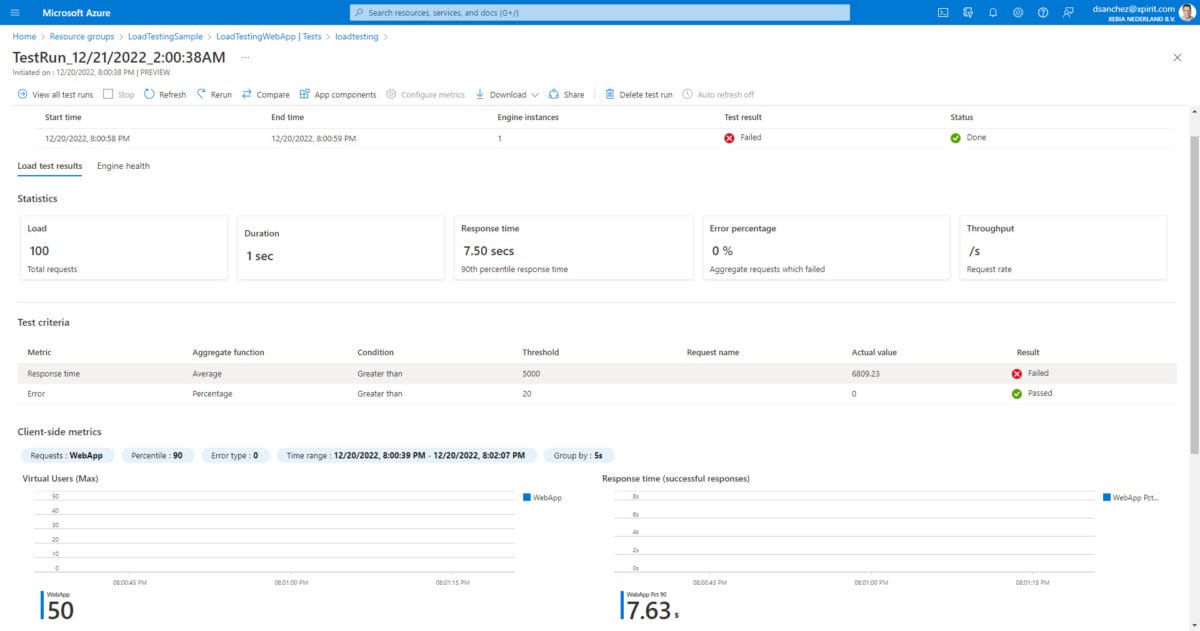

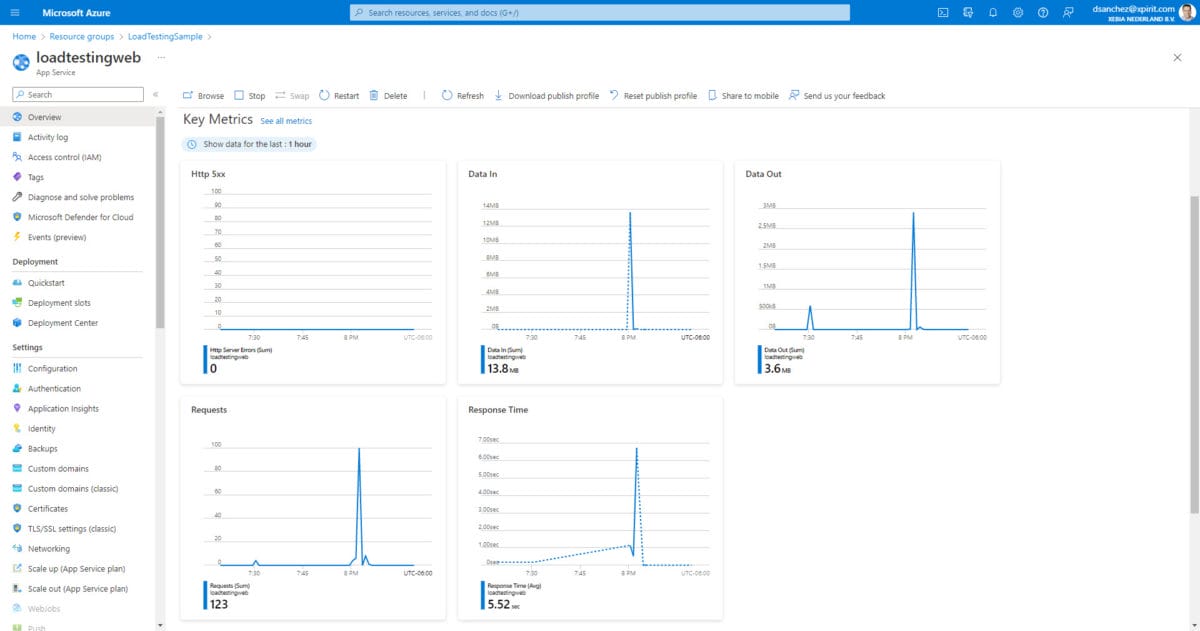
In the Azure App Service, we can see the metrics with the response times (higher than 5 seconds) and the number of requests with the Data in and Data out. Here is a screenshot of the key metrics in Azure Portal:

In addition, I added Application Insights to monitor the web app. In the Azure Portal we can see the performance issues and failures. Here is a screenshot of the performance section for the web application:
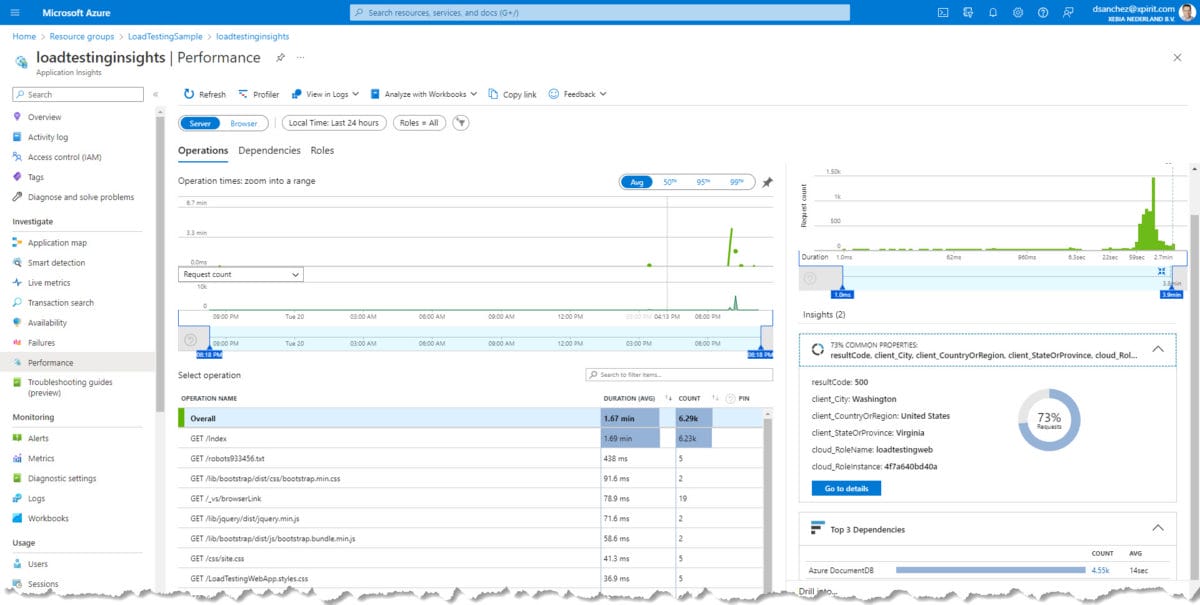

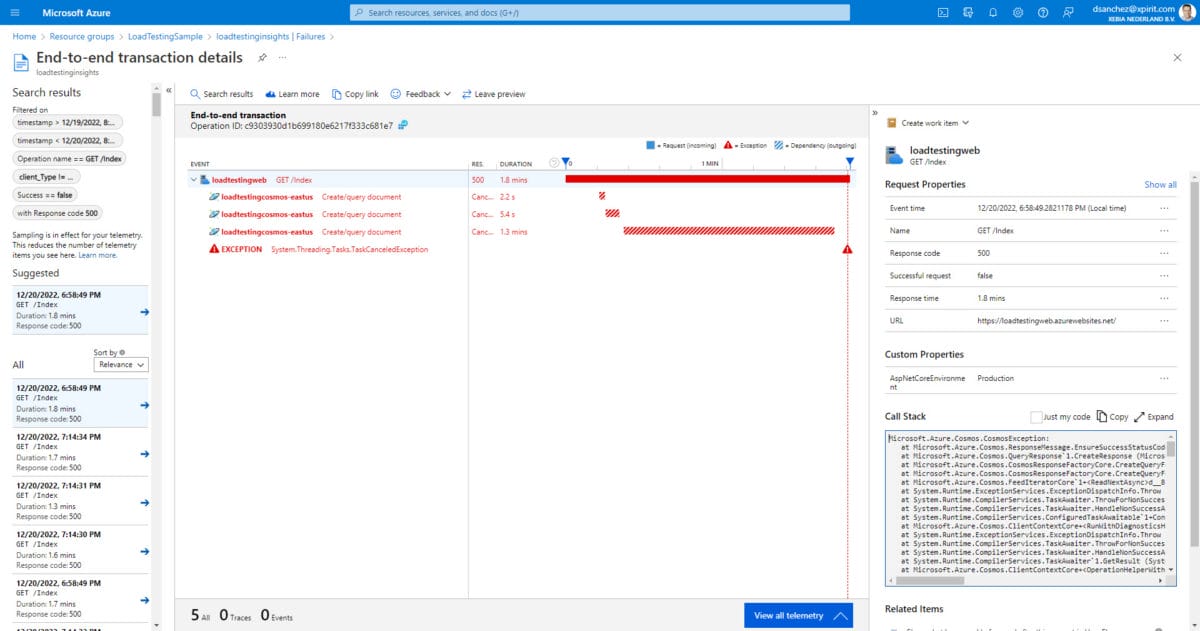
From the image above you can see where the requests came from. In this case, I am running Azure Load Testing in the East US region (Virginia). Here is a screenshot of the exception captured in the transaction:

Conclusion
Load Testing should not be run in a production environment. Try it in a Dev/Test, QA, or pre-production environment. Even if you are running on deployments slots, remember that the web app will still run on the same App Service Plan, and this could affect your production environment or cause a Denial-of-Service Attack.
If you would like to learn more about Azure Load Testing, I recommend you review the service documentation.