5G is often associated as something closely related to smartphones and the market of individual users. Practically, however, 5G is an all-embracing technology that will boost the interaction between people and machines in many different areas – and in an unprecedented way.
One of the 5G-related areas that’s gaining interest remarkably quickly is Industry 4.0, with Smart Factories and Smart Manufacturing being at the forefront. In this entry, we’re going to take a look at how the latest mobile network generation can empower these operations.
Industry 4.0 – Which Areas Need Support?
For some time now, modern manufacturing has been facing many challenges. Competition is fierce and imposes to optimise processes continually. Market demand shifts swiftly and calls for flexibility of production. Specific sectors are now heavily regulated and need the demonstration of traceability of the final product. That’s why the mentioned Industry 4.0 – which is pushing towards ever-present automation – is gaining momentum.
The origins of the fourth industrial revolution date back to 2011. Significant recognition came around 2015. The four fundamental design principles at stake are interconnection, information transparency, technical assistance, and decentralised decision-making. The common denominator of those is efficient communication.
And that’s where 5G can make such a big difference.
5G – What Can it Change in Manufacturing?
The latest generation of the cellular network was designed as a universal, efficient, fast, and flexible network for machine-to-machine communication. It’s two orders of magnitude faster than the previous generation. Simultaneously, it can connect up to one million devices per square kilometre.
The core network offers Edge Computing power for hire in the form of MEC servers. The latency dropped to the range of a single-digit millisecond. The connection reliability is similar to that of a fixed cable. The network can be sliced into private chunks. Power consumption is reduced.
All this combined opens an entirely new set of possibilities for smart factories.
Cable-Free Flexibility
To connect robots, sensors and other devices with itself and with the control equipment, most factories still rely on hundreds of miles of cables. Wiring doesn’t come for free and requires regular maintenance. What’s perhaps even more critical, cables are difficult to change once laid. Moving them costs money, time, and often requires re-certification. Using 5G gets rid of these problems.
Another benefit lies in usability. Wiring is also not always a perfect solution. Certain devices need mobility which physical cables may not be able to fully provide (or even not at all). Moreover, a wireless device can be moved to a different spot without much effort. And the ability to efficiently reconfigure a factory to a new or customised product is of utmost importance in the world of rapidly changing requirements and savage competition.
Unparallaled Insights
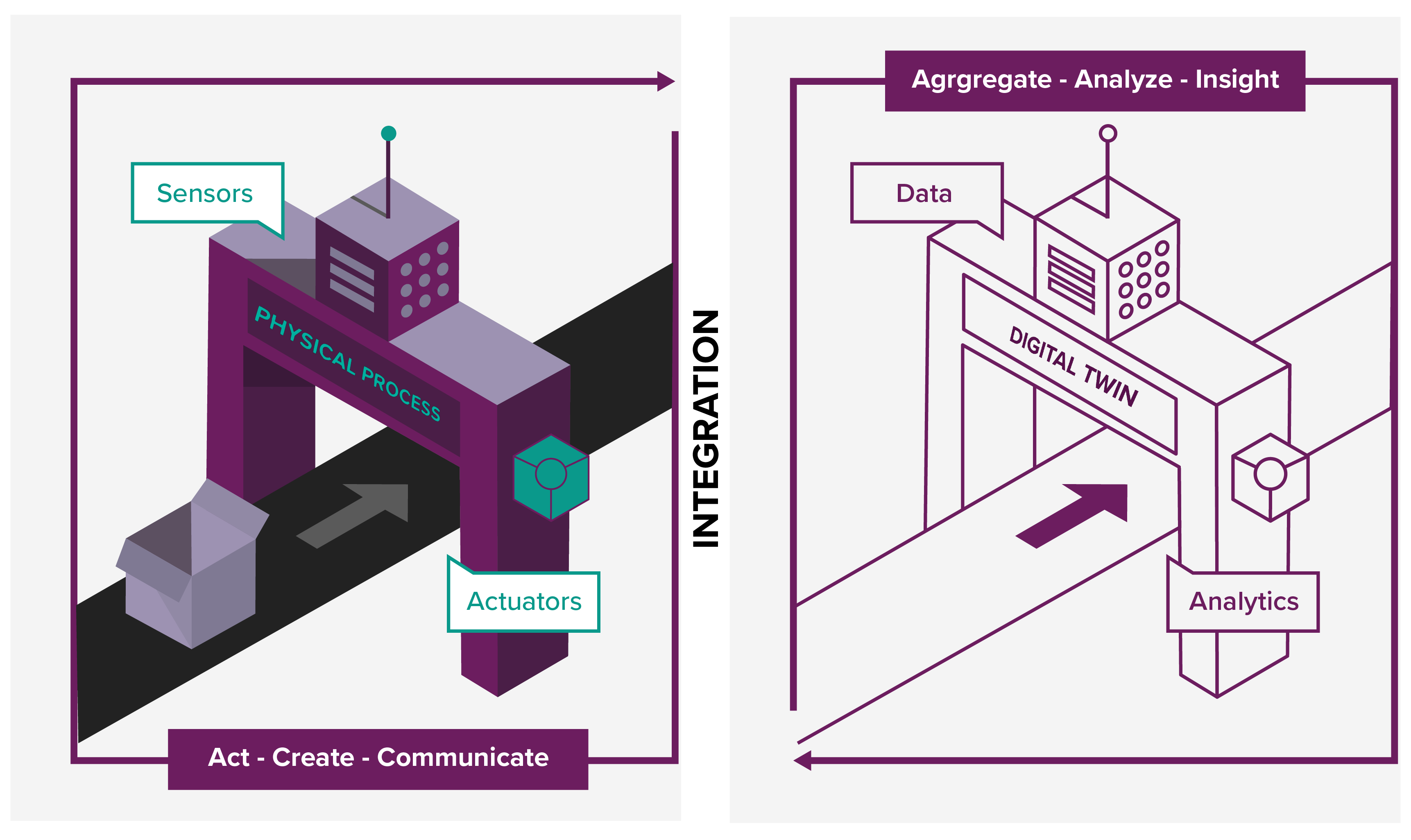
A high-speed, low-latency network connected to multiple sensors monitoring the factory provides plenty of useful insights.
This stream of Big Data can feed Machine Learning models to assist the factory floor with split-second decision making – all thanks to the power of the Edge Compute located close to the factory. For advanced, longer-term optimisation and insights into the production chain, the data can be directed to the Cloud to further train the models, which requires massive computing capacity.
Moreover, Digital Twins – a mirror of a physical device in an IT system – helps to visualise the current factory state for human inspection. Certain sectors, like pharmaceutical manufacturing, are heavily regulated and need to demonstrate traceability and observability of what’s happening. A high-resolution video feed helps with intricate quality control – especially for low-volume, high-margin industries. Closely monitoring of parameters of critical equipment allows the prediction of components failure and dynamic scheduling of preemptive maintenance to avoid slowing down or stopping the production.
Augmented Control
A minimal latency in the range of single-digit millisecond is key to Augmented Reality and maintaining the illusion of real-time. With smart glasses, people on the factory floor can immediately receive additional information about what they are currently looking at – whether it’s a part of a production line checkpoint that needs to be inspected or a particular device that requires troubleshooting.
Logistics companies currently test Smart-Guided Picking in their warehouses to optimise manual package handling. With the help of this system, a warehouse operator doesn’t have to be at the same place, building, or… even country. Using futuristic equipment – like a robot arm – the operator can control the entire process remotely, with a previously unthinkable precision.
This is especially important in distributed value creation chains when the number of experts that can perform demanding tasks or consultation is sparse. Manufacturers of bespoke machinery appreciate an option to remotely assist or provide training for their customers on their sites, which often happen to be secluded and hard to visit personally.
Autonomous Ground Vehicles
AGVs provide efficiency and flexibility when it comes to moving packages, parts, or products across the factory floor or nearby outdoors. To successfully navigate in a complex and dynamic environment with many other moving parts, it’s crucial to be able to coordinate a large number of vehicles and communicate with them simultaneously.
Heavy calculations for routing algorithms may be offloaded to Edge Computing servers located nearby within the core telecommunication network with enough power to run them quickly. Thanks to 5G’s low latency, the results can be applied in near real-time.
Pinpointing the exact geolocation of vehicles is essential for smooth and safe traffic. 5G offers an out of the box solution in that regard – it’s capable of a horizontal plane positioning accuracy of just a few centimetres; much better than in the previous generation.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C9qhdjKHgXA&feature=youtu.be
Security and Safety
Switching from internal communication mechanisms to public 5G is usually coupled with one significant concern – security. However, this concern is not necessarily justified.
5G offers a mechanism called network slicing. With it, the individual range of frequencies in a given region can be allocated to a single customer exclusively. This effectively creates a private, physically isolated network that can be further divided to separate critical industrial communication from corporate traffic. It can also allow easy external connectivity for suppliers to provide maintenance without setting up complex firewall rules.
Aside from cybersecurity, the physical security of people on the factory floor is inarguably even more critical. More connected devices and a higher bandwidth result in more data that can be used to detect threats early, like fire hazard, heavy equipment malfunction or unauthorised intruder presence. Edge Computing and AI help processing this additional data locally and automatically react to threats.
In general, the growth of automation and remote control limits the need for people to be in potentially dangerous areas. Low latency allows the operator to stop the robotic arm a fraction of a second sooner, which may sometimes prevent damage or injury. Ultra-high reliability of the 5G network reduces the risk of an incident caused by the potential loss of connection.
And More
In this entry, we mentioned only a few major benefits of 5G at a Smart Factory. There’s, of course, more, and the spectrum of possibilities and innovation is continuously growing.
For example, a 5G receiver requires much less power than in the previous generation. The battery of these devices can last significantly longer, reducing maintenance cost (assuming, of course, that the device is not autonomous enough to charge itself!).
As the automotive industry reports, the high bandwidth also simplifies uploading and updating firmware in an increasing number of the smart machine or product parts. Waste reduction aids not only companies’ budgets but also helps to keep the environment cleaner.
Connectivity is essential not only on the factory floor and the nearest vicinity, but also across the entire supply chain up to the user of the product. Tracking the location of parts and machines and their condition before they reach the factory may prevent surprises and slowdowns in production lines.
5G is also an opportunity to unify and integrate a fragmented and limited supply chain connectivity with smart factories. On the other end of the equation, monitoring products on customer premises helps to deliver better service in many industries.
What Holds the Future?
The industry is changing as we speak, and 5G is at the heart of it. Or, should we say – at the nervous system?
With the increasing manual work costs around the world and progressing automation, the global value chain is on the verge of revolution. Some changes are already in motion, with South Korea’s industry-leading the pack.
It’s not out of the question that factories will physically relocate back to their historical origins – closer to customers. With the growth of specialized hardware and software, the work market will likely call for different skills. The ability to facilitate efficient communication between various systems and devices, automate, gather the data – and learn from it – will be increasingly sought after with the rise of collaboration opportunities between physical goods manufacturers and software vendors.
Sources
https://www.industryweek.com/technology-and-iiot/article/22026384/5-ways-5g-will-power-the-smart-factory-of-the-future
https://www.gsma.com/iot/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/2020-04_GSMA_SmartManufacturing_Insights_On_How_5G_IoT_Can_Transform_Industry.pdf
https://images.samsung.com/is/content/samsung/p5/global/business/networks/insights/white-paper/5g-untethering-smart-manufacturing-operations/white-paper_5g-untethering-smart-manufacturing-operations.pdf
https://www.cnbc.com/2020/07/11/5g-spurs-factory-automation-could-add-trillions-to-economy.html
https://www.business.att.com/learn/tech-advice/how-5g-will-revolutionize-manufacturing.html#
https://www.ericsson.com/en/news/2018/1/5g-manufacturing—tallinn
https://www.bosch.com/stories/5g-industry-4-0/
https://techwireasia.com/2020/07/why-koreas-telcos-are-developing-5g-smart-factory-solutions/
https://www.5tonic.org/news/5g-technology-applied-asti-mobile-robotics-agvs
https://www.pgs-soft.com/blog/top-5-reasons-to-use-mesh-twin-learning-in-your-smart-factory/
https://www.pgs-soft.com/blog/industry-4-0-where-the-world-is-going/
https://www.connectivity.technology/2020/03/5g-indoor-precise-positioning.html
https://www.lightreading.com/the-first-network-slice-trial-for-intelligent-manufacturing-how-does-the-value-of-5g-reflect/a/d-id/755526 [:]