Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Deep Learning (DL), are the most common tech buzzwords yet most commonly confused with each other. Whilst having a close connect, these terms cannot be interchanged and used.
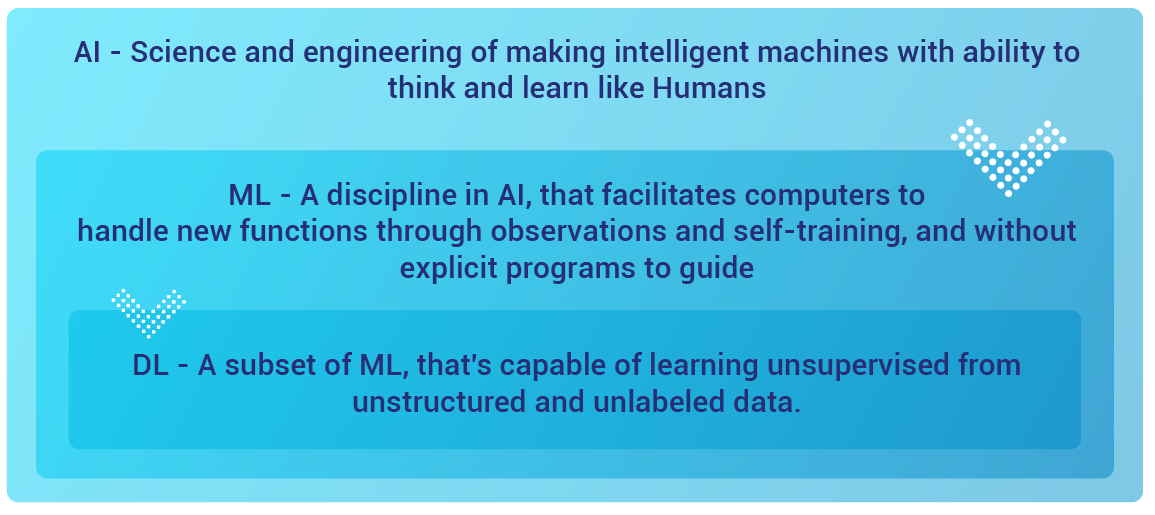
AI, ML, and DL – The Connection
In simplest terms possible, AI is the superset, ML is a subset of AI, and DL is a subset of ML.
The age old industrial revolution has extended human mechanical power, this new age revolution, the second machine age is going to extend our cognitive abilities, our mental power through Artificial Intelligence.
History of Artificial Intelligence – The Inception
The industrial revolution has increased our According to John McCarthy, an American Computer Scientist and Cognitive Scientist, Artificial Intelligence is the “science and engineering of making intelligent machines”. Simply put, AI is all about mimicking human behaviour in various methods predominantly about thinking and learning.
In 1956, John McCarthy organized the Dartmouth Conference, at which the term AI – Artificial Intelligence was first adopted. AI was promoted globally as the science that could transform the world. In the day, the primary goal of AI was to assist computers to carry out tasks that were exclusively humanly possible, precisely, the tasks that needed brains to act. In the 90’s the Japanese government with the help of AI enthusiasts carried out tasks with AI that could translate languages, identify pictures, and also understand logics like humans (although not in par).

This was a beginning of an era that made corporations and governments turned heads towards AI and start funding niche project. Over the course, giants like Amazon and Google powered up with AI by leveraging data to understand customer behaviour and patterns.
When calculator did not replace humans, how would AI?
Unlike the misconception of millions of people, AI will not replace humans, it can only automate and simplify a repetitive human task that needs mere logic/reasoning.
Machine Learning According to an article by McKinsey, ML is described as ‘technology based on algorithms that can learn from data available rather than solely depending on rules-based programming’. However, with all the volumes of Data available today, comprehending data and drawing relevant analysis that sums up to productive results isn’t an easy task. Hence, similar to the way humans experience, observe, and respond, computers being programmed to experience the world around, observe and take action through ML.
For instance, let’s take a basic example of how we teach kids to speak. You do not start teaching a kid by handing over a book on ‘How to speak in 30 days’ right? Instead, you keep talking to the kid; start with vowel sounds and then slowly progress to basic words like mom, dad, so on and so forth. With time, when you show the kid an apple, the kid identifies it, whether the apple is green or red, big or small, etc. ML too follows a similar approach. The computer is fed with huge volumes of data; machine learning works with it to see what comes out.
It doesn’t come as a surprise that companies like Amazon and Netflix uses machine learning to suggest you the products that you might want to buy or movies you would be interested in watching.
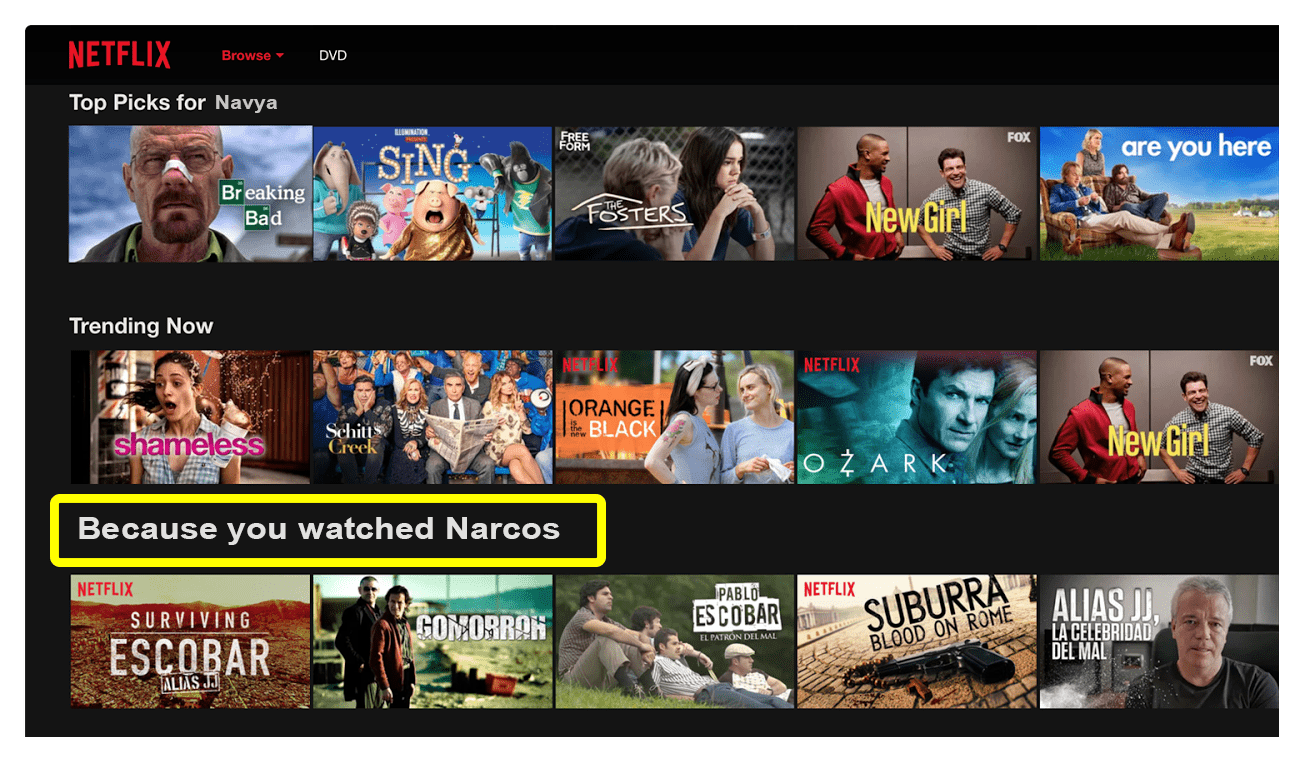
LinkedIn and Facebook are eerily hinting who your friends might be and you have no idea about how they do it (till AI gained popularity). These are the core algorithms that machines have learnt from data rather than being programmed. Machine Learning is also the driving force that made self-driving cars possible today. The first tested self-driving car by Google has travelled over millions of miles without any accidents on regular used roads solely guided by Machine Learning.

Deep Learning
Deep Learning (DL), a subset of machine learning, is all about Neural Networks. To train the neural networks of deep learning, we input heaps of data, and compare its outputs with outputs from the dataset. Though we still haven’t reached a phase of imitating a human brain, we are heading in the right direction.
How deep learning works:
For instance, if you are given an image of a dog, you identify it as a dog irrespective of the breed, whether it is standing, sitting or sleeping, or even if it’s dressed up with a lion’s mane.

ML & DL– The Difference
The core difference between ML and DL is that ML models needs guidance even on making progressive changes. If ML hits a dead end, or make an incorrect prediction, programmer will have to manually correct the bug while DL can work it out on its own. To understand this better, we need to deep dive into Supervised and Unsupervised learning.
As the name indicates, supervised learning is done in the presence of a teacher or a supervisor and unsupervised is without one.
Unsupervised learning: Let’s take the example of a 2-year-old child. When she drops a ball, she knows that it is going to fall down, and when she spills water, she expects the resulting mess. There is no need for her parents to teach her Newton’s laws or differential equations or so-called basic instincts. The child discovers all these theories on her own, in an unsupervised way. Unsupervised learning has been a challenge for AI and it may take several few more years to ideate easier methods to untangle the knot. Unsupervised learning is about trying to discover representation of data.
Supervised learning:

Supervised vs Unsupervised learning
The advantage of unsupervised learning over supervised learning – unsupervised learning allows computer to project themselves in to the future to generate probable futures, mostly conditioned on current situations and scenarios. This allows computers to reason and plan ahead even for circumstances that they have not been trained. In case of supervised learning, we will have to teach computers all kinds of circumstances, and how humans react in those situations.
For instance, let’s consider the training process of self-driving cars. How does a human learn to avoid an accident and dangerous driving behaviour? One cannot go through thousands of accidents, unlike how we teach machines. What we need is to generate plausible images and plausible futures.
Machines are being trained to generate new images that computers have never seen or were trained on, but are plausible. Our machines self-teach themselves on how to avoid dangerous situations and probably reaction humans would have to any probable mishaps.
Conclusion
Every industry that understands the importance of data is now jumping onto the AI bandwagon. To name a few…
- Medical research – to detect cancer cells or identify any anomalies in a human anatomy
- Manufacturing – to improve safety of workers around heavy machinery
- Electronics – to assist in day to day activities like Siri, Alexa, and Google Home
- Retail – to enhance customer experience by providing personalized suggestions
- Transportation – to identify key trends and patterns and create subsequent routes
Like most humans never imagined, AI now has the ability to comprehend, automate, assess, and foresee, which is most powerful thing a computer could do so far in history. AI is the unapologetically going is the next big thing that organizations have already laid eyes on.
Are you struggling to find a peace with your data and unable to step up your game? AI is your way to go and coMakeIT can help you get places you’ve never imagined!
Let’s chat up!





