
Cloud services offer incredible accessibility and scalability. But they come with a fundamental challenge: you need to move your data to the cloud first. This data migration presents significant challenges, such as bandwidth constraints, transfer costs, compliance requirements, or security concerns. But what if you could bring cloud services directly to where your data already resides? That is exactly what Google Distributed Cloud Connected (GDCC) delivers.
What is GDCC
Google Distributed Cloud Connected (GDCC) is a fully managed edge cloud solution and part of Google’s broader Google Distributed Cloud (GDC) portfolio. It brings Google Cloud’s infrastructure, services, and APIs directly to your data centers, edge locations, or other environments. The key advantage of GDCC is simple but powerful: your data stays on-premises while you gain access to Google Cloud’s advanced capabilities. This solves critical challenges for organizations with strict data sovereignty requirements, latency-sensitive applications, or operations in locations with limited connectivity.
GDCC is built on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), providing a consistent and modern cloud experience across hybrid, edge, and on-premises environments. It’s ideal for organizations that need to meet strict compliance requirements, want to reduce latency, or process data locally due to connectivity constraints.
What GDCC is not
❌ It’s not a replacement for public cloud. GDCC is designed for specific use cases where public cloud isn’t feasible.
❌ It’s not just another edge computing solution. GDCC is a fully managed service with Google Cloud’s security, AI/ML, and data analytics capabilities built-in.
❌ It’s not a one-size-fits-all solution. GDCC is tailored for industries and scenarios with strict data sovereignty, latency, or connectivity requirements.
Use cases for GDCC
How does GDCC translate into real-world impact? Let’s dive into some of the key scenarios where GDCC can make a difference for your organization.
Managing data-intensive workloads cost-effective
Applications that generate or process large volumes of data, such as media streaming, IoT, or scientific research applications, often face challenges when transferring data to and from the cloud. The costs and time associated with moving massive datasets can be prohibitive.
GDCC allows organizations to process the data locally, reducing the need to transfer large volumes of data to the cloud. This not only improves performance, but also optimizes costs. For example only processed data, most often in an aggregated and smaller format, can be moved to the cloud.
Complying with data sovereignty and regulatory requirements
In many industries, such as healthcare, government, and finance there are strict regulations that require data to remain within specific geographic boundaries or on-premises. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines, legal consequences, and loss of customer trust.
The benefit of GDCC in such cases is that with GDCC you can keep your data on-premises, while still leveraging Google Cloud’s infrastructure and services. This ensures compliance with local laws and regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA, without sacrificing the benefits of cloud computing.
Ensuring uninterrupted operations on stable network connections with ultra-low latency
Many mission-critical applications, such as those in manufacturing, healthcare, or financial services, rely on consistent and stable network connectivity. Even minor disruptions can lead to significant operational downtime, lost revenue, or compromised user experiences. Latency spikes or jitter can degrade performance, leading to poor user experiences or even system failures.
Google Distributed Cloud ensures a stable and reliable network connection by enabling organizations to run applications on-premises or at the edge. This eliminates the risks associated with internet-based data transfers, such as packet loss or connectivity issues, ensuring uninterrupted operations even in challenging environments. With support for high-performance networking technologies like SR-IOV and DPDK, GDCC enables organizations to achieve the lowest attainable latency for even the most demanding applications
Limitations
While GDCC offers a powerful solution for running workloads at the edge or on-premises, it’s important to understand its limitations to ensure it aligns with your organization’s needs. Here are some key considerations:
Workloads must be containerized
GDCC operates on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), which means your workloads need to be containerized to run on the platform. Even though this aligns with modern cloud-native practices, it may require some organizations to refactor or adopt existing applications to fit on a containerized architecture. Additionally, teams will need a certain level of maturity and expertise in Kubernetes to effectively manage and deploy workloads on GDCC. For organizations new to Kubernetes, this could involve a steep learning curve and potentially additional training or hiring to build the necessary capabilities.
Limited processing capacity
Unlike on-demand scaling in the cloud, GDCC has fixed processing capacity based on the hardware configuration you choose. This means you need to carefully plan and allocate resources to avoid overloading the system. While GDCC is designed to handle demanding workloads, it’s not infinitely scalable like a public cloud environment. When demand increases it is important to order extra hardware in time.
Connected Vs. Air-gapped
Google Distributed Cloud offers two distinct deployment models to address different operational and regulatory needs:

Connected deployment
The Connected Deployment maintains a link to Google Cloud, enabling organizations to leverage Google’s managed services, real-time updates, and advanced tools like AI/ML and data analytics while keeping data and workloads on-premises or at the edge. This model is ideal for businesses that require a hybrid cloud setup, where seamless integration between on-premises and cloud environments is critical. For example, a retail chain might use a connected deployment to process customer data locally in stores while synchronizing insights with Google Cloud for centralized analysis.
Air-gapped deployment
The Air-Gapped Deployment is designed for organizations with the most strict security and compliance requirements. It operates entirely offline, with no connectivity to Google Cloud or the public internet, ensuring complete isolation and control over data and infrastructure. This model is particularly suited for highly regulated industries like defense, healthcare, or government, where data sovereignty and offline operations are non-negotiable.
Whether you need the flexibility of a connected environment or the absolute security of an air-gapped setup, GDCC provides the tools and infrastructure to meet your unique needs.
Rack Vs. Server
GDCC is available in two hardware form factors, each tailored to different scalability and performance needs:

Rack
The Connected Rack is a high-capacity, scalable solution designed for large-scale, data-intensive workloads. It consists of multiple servers, top-of-rack switches, and networking components, making it ideal for environments where processing power, storage, and redundancy are critical. For instance, a manufacturing plant with complex IoT systems might deploy connected racks to handle real-time data processing and predictive maintenance at scale.
Server
The Connected Server is a compact, standalone unit perfect for smaller-scale deployments or remote edge locations. It’s a cost-effective option for organizations with limited space or infrastructure, such as a retail store analyzing in-store customer behavior or a remote oil rig monitoring equipment performance.
Both options deliver the same core capabilities of GDCC, but the choice between them depends on the scale of your operations, the complexity of your workloads, and the physical constraints of your environment. Whether you need the expansive power of racks or the simplicity of servers, GDCC ensures you have the right hardware to meet your goals.
Supported GCP services
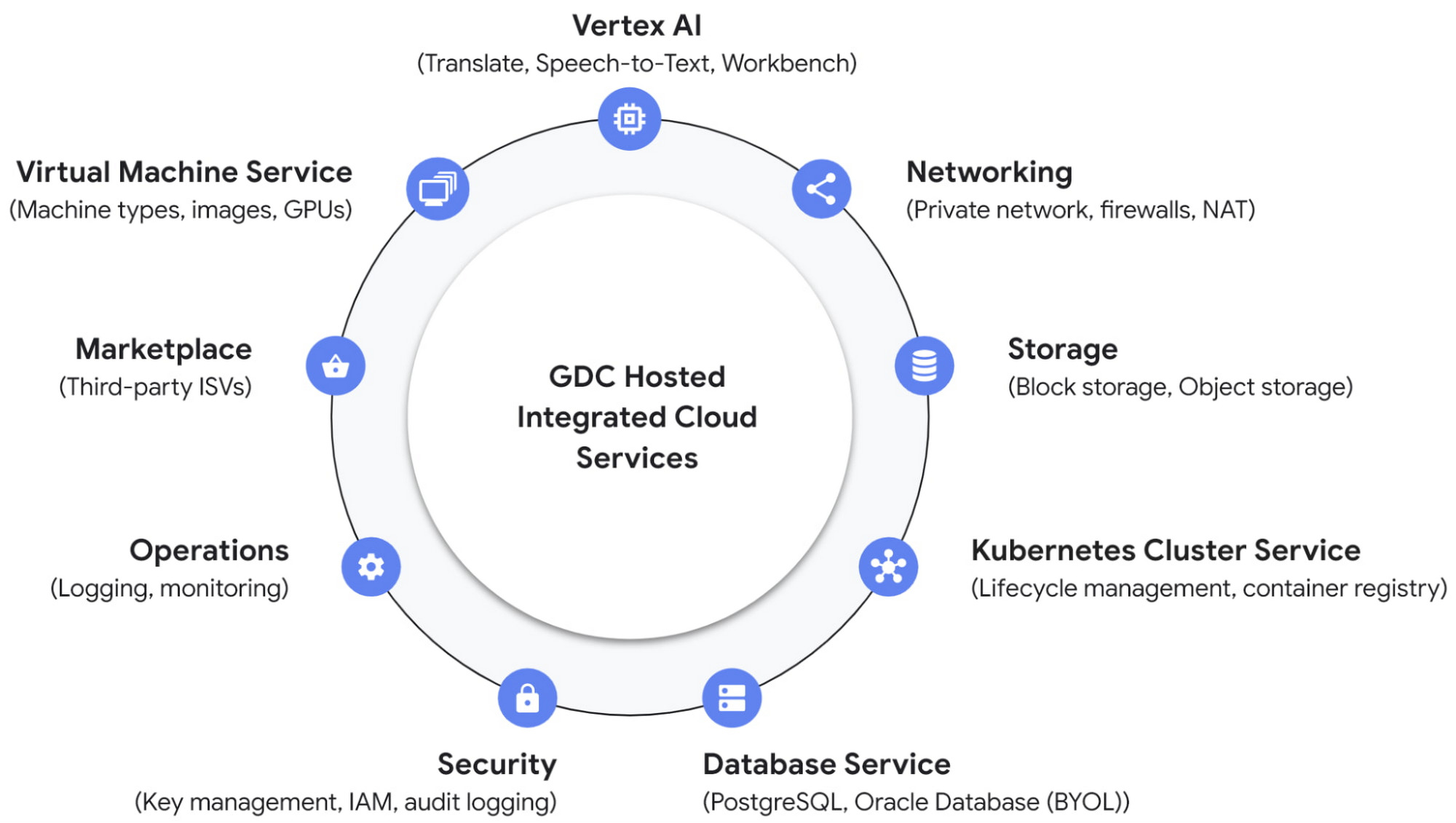
Google Distributed Cloud (GDC) aims to deliver a full-stack cloud experience on-premises, combining Google Cloud’s infrastructure, security, and services with the flexibility of edge and data center deployments. It supports a wide range of managed services, including:
Compute & Orchestration: Run containerized workloads with Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) or deploy virtual machines with GPU support for high-performance applications.
Storage: Choose from block or object storage options tailored for low-latency edge processing or large-scale data residency needs. There is support for databases like AlloyDB Omni as well.
Networking: Built-in firewalls, VPNs, and NAT ensure secure connectivity, while integration with Google Cloud’s backbone enables hybrid workflows.
AI/ML & Analytics: Deploy AutoML models in containers, allowing to run trained machine learning models locally at the edge.
Security & Compliance: Inherit Google Cloud’s IAM, KMS, and audit logging, with optional air-gapped deployments for regulated industries.
Observability: Unified logging, monitoring, and diagnostics via Cloud Operations, providing visibility across distributed environments.
Marketplace: Access third-party ISV solutions and Google’s first-party services to extend functionality.
To keep track of the supported google services, check out the Supported
Services page.
How do I get GDCC into my data center?
Deploying GDCC in your data center or edge location is a straightforward process, but it requires careful planning and collaboration with Google Cloud experts. Here is a high-level overview of the steps involved:
- Assess your needs: Work with your team and Google Cloud representatives
to evaluate your workload requirements, hardware needs, and compliance
considerations. - Choose and order your hardware: Select the appropriate GDCC hardware
configuration (connected racks or standalone servers) based on your
processing and scalability requirements. - Deploy the hardware: Google or a certified Systems Integrator (SI) will
install and configure the hardware in your data center or edge location. - Set-up networking: Your network administrator will configure the
necessary networking components to ensure seamless communication between
GDCC, your local network, and Google Cloud. - Provision cluster(s): Use Terraform (recommended), the Google Cloud
console, or CLI to provision GKE clusters and deploy your workloads. - Monitor and optimize: Leverage Google Cloud’s monitoring and management
tools to ensure optimal performance and resource utilization.
Google Cloud provides end-to-end support throughout the deployment process, ensuring a smooth transition to GDCC.
Future of GDC
Google Distributed Cloud is rapidly evolving to bridge cloud and edge environments. The upcoming integration of Gemini AI (coming to GDC in Q3
2025) marks a major step, bringing Google’s most advanced generative AI to air-gapped and regulated deployments.
While Google hasn’t shared a public roadmap, I expect more core GCP services, like Cloud Storage buckets, Dataproc, and expanded managed database options (beyond the current AlloyDB Omni preview), to arrive at the edge soon.
To keep up-to-date with the latest features of GDC you can check out the most recent release notes.
Conclusion
GDCC represents a paradigm shift in cloud computing. Instead of bringing your data to the cloud, it brings Google Cloud to your data. This approach combines the best of both worlds: the security and control of on-premises infrastructure, with the innovation and power of widely used Google Cloud services. While GDCC is not a replacement for public cloud, GDCC offers a compelling solution for organizations with unique regulatory requirements, latency concerns, or edge processing needs.
Ready to explore how GDCC can transform your business?
Contact us today to learn more or schedule a consultation.
Photo by Andreas Rasmussen on Unsplash





